Source: Tongji Accounting Medical Management New World Author: Dai Xiaozhe
Based on the analysis of the influence of DRG package payment on hospital cost accounting, taking tongji hospital as an example, this paper introduces the hospital’s experience in carrying out cost accounting under DRG payment system according to the requirements of promoting DRG pilot, including: design of cost accounting implementation scheme, basic data governance (unified classification information of cost categories, establishment of bottom data of cost elements, requirements of cost data integration), data modeling of income analysis, modeling of cost accounting rules, and analysis of DRG composition cost, which can be used as a reference for all localities to carry out DRG payment.
Diagnosis Related Groups (DRG) is a combination classification scheme that classifies patients into several diagnosis groups according to the clinical characteristics such as hospitalization days, major diagnosis, minor diagnosis, complications, complications, surgical operation, disease severity and prognosis, resource consumption, and social characteristics such as patients’ age and gender.
DRG pays to divide the cases with similar clinical process and similar resource consumption into the same DRG group, and calculates the cost standard of each DRG group in combination with evidence-based medicine, and provides the hospital with a fixed advance payment for acute inpatients in groups. The Guiding Opinions of the General Office of the State Council on Further Deepening the Reform of the Payment Method of Basic Medical Insurance (Guo Ban Fa [2017] No.55) puts forward: "The state has selected some areas to carry out pilot payment by DRG, explore the establishment of a DRG payment system, and mainly pay for inpatient medical services by DRG."
The Notice on Printing and Distributing the List of National Pilot Cities Paying by Groups Related to Disease Diagnosis (No.34 [2019] of Medical Insurance) points out: "The 30 national pilot cities paying for DRG should complete the tasks of each stage according to the idea of’ top-level design, simulation test and actual payment’ to ensure the simulation operation in 2020 and start the actual payment in 2021.
On the basis of uniformly using the codes of disease diagnosis, surgical operation, drugs, medical consumables and medical services formulated by the state, improve the DRG payment information system and handle the data interface with the hospital. "Notice of National Pilot Technical Specification and Grouping Scheme for Payment of Disease Diagnosis Related Grouping (DRG) (No.36 [2019] of Medical Insurance Office) published the Technical Specification for Grouping and Payment of National Medical Insurance DRG and the Grouping Scheme of National Medical Insurance DRG(CHS-DRG), and the top-level design of DRG in China was basically completed.
The unification of DRG payment for medical insurance in hospitals across the country indicates that the payment mode of hospitals will be mainly based on project payment and mainly based on DRG payment. The 2020 National Medical Security Work Conference emphasized that the DRG pilot should be further promoted in 2020. "Opinions of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China and the State Council on Deepening the Reform of Medical Security System" points out: "Promote the payment in groups related to disease diagnosis". Based on the practice of tongji hospital, this paper discusses the cost accounting under DRG payment, which can be used as a reference for other places to carry out DRG payment.
Influence of DRG payment on hospital cost accounting
The core idea of DRG case classification scheme is to group cases with the same characteristics in one respect, and the classification is based on the patient’s diagnosis. On this basis, the influence of factors such as patient’s age, operation or not, complications and complications is considered, and the hospital’s treatment of patients is related to the expenses incurred, which provides a basis for the formulation of fixed payment standards for each group through scientific calculation.
Based on the idea of case-mix, the scheme comprehensively considers the individual characteristics of cases, divides cases with similar clinical processes and similar resource consumption into the same group, adjusts the risk of each group, gives relative weight, and establishes a structured patient grouping coding system and standardized evaluation indicators, thus reflecting the output, efficiency and quality of medical services.
Under the DRG payment system, considering the complexity of patients’ illness, each case in each disease group has similar clinical characteristics and consumes similar medical resources, the cost of each disease group is calculated according to a certain cost-cost ratio, and the rates of various diseases are formulated with reference to the pricing principle of public utility products. Each DRG corresponds to a cost weight calculated according to the average treatment cost of patients. With a unified cost accounting method, we can master the cost of treating diseases and formulate a reasonable fixed payment standard for hospitals. The cost analysis of DRG patients can standardize the output of medical services and make the clinical characteristics and cost consumption characteristics of patients in the same group more comparable.
1. Paying by DRG exerts external pressure on hospitals to control operating costs.
According to the DRG payment system, a fixed payment standard is set for each DRG group, and the complicated and random medical payment process is standardized, and the payer no longer pays according to the actual cost of the patient’s hospitalization (that is, medical service items). After the main diagnosis and treatment methods of inpatients are determined, the hospital can know in advance the standard of fees that can be charged to patients or paid by medical insurance.
The fixed rate for specific diseases set in advance is calculated according to the treatment cost of similar diseases. Although it will be adjusted appropriately due to institutional planning, nature and regional differences, it will not change or loosen due to the actual cost of the hospital. Under the constraint of the hard budget of prepaid rate, service providers must consciously implement diagnosis and treatment in the most efficient way in order to obtain income higher than the social average.
If the hospital conducts diagnosis and treatment at a cost less than the charging standard, the difference will form an institutional balance of income and expenditure. On the contrary, if the treatment cost is higher than the established rate, the hospital will suffer economic losses. The basic logic of paying by DRG is that the medical insurance income obtained by the hospital is certain for specific patients and treatment methods, but to increase the medical surplus, the hospital should start from the cost under refined management.
DRG payment divides inpatients into a certain number of disease groups according to their clinical similarity and resource consumption similarity, determines service units based on the information on the front page of medical records, calculates the cost rate of each service unit in combination with cost drivers, calculates the average cost of each disease group according to the expenses incurred by each unit and the cost rate, and formulates the prepayments for medical expenses according to the groups.
When designing the DRG payment system, the price standard of packaged payment was determined, which extended the focus of supervision from front-end medical service items, selection of drugs and medical consumables and price control to medical safety, quality and effect, and mobilized the enthusiasm of hospitals and medical staff to improve medical safety, quality and control costs, reduce waste and expand the balance by using the payment economic lever of fixed price and retained balance.
Paying by DRG will transfer the economic risks in medical activities from patients to hospitals. In order to make profits, hospitals must improve medical quality and operating efficiency by shortening hospitalization days, reducing induced medical treatment and strengthening standard clinical pathway, and bear the pressure of operating costs.
2. Payment according to DRG has proved to be effective in controlling hospitalization expenses in various countries.
The United States, Australia, Germany, France and other countries have formulated their own DRG versions, defined the grouping, coding, cost and price scheme of DRG, and carried out payment practice. As a widely used payment method for acute inpatients in the world, DRG has been incorporated into the domestic payment system as an important hospital payment method in more than half of the countries of the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD).
The main expected purposes of introducing DRG in various countries are: to improve the transparency of medical services, to facilitate hospitals and medical insurance to monitor medical consumption, and to identify efficient services; Encourage efficient and low-cost medical behavior and encourage efficient use of resources. Practice shows that paying by DRG is effective in controlling hospitalization expenses.
Since October 1983, the United States has adopted the DRG prepayment system in the hospitalization service of Medicare, setting a fixed compensation standard for acute inpatients, and paying a fixed fee to the hospital according to the diagnosis and classification of the patients when they are admitted to the hospital, instead of paying the fee according to the number of days of hospitalization or the specific medical services they receive in the hospital. No matter how many times the patients check their equipment in the hospital and what services they receive during their hospitalization, the hospital will get the same compensation.
If the patient stays in hospital for a long time or uses expensive services, the hospital can’t get compensation. Because of the cost risk, the hospital is put under certain financial pressure by medical insurance, and the budget constraint is greater when treating patients, thus reducing unnecessary examination and medication, reducing medical expenses, shortening the average hospitalization days and improving medical quality.
The reform of payment mode in China, which takes DRG payment as the breakthrough point, aims to pay with the pre-set quota of the same group of cases, so that drugs, consumables, examinations and tests become the cost of treating diseases, rather than the source of hospital income, so as to stimulate hospitals to actively control costs, eliminate the profit-seeking tendency of income from selling drugs, consumables and examinations, abide by the technical specifications and operational specifications of clinical diagnosis and treatment, and obtain medical insurance through appropriate technology and drugs, treatment due to illness, reasonable examination, rational drug use and reasonable diagnosis and treatment.
3, according to the DRG pricing payment need to formulate the corresponding hospital cost accounting rules.
"Basic Guidelines for Cost Accounting of Public Institutions" (Cai Shui [2019] No.25) points out: "In order to meet the demand for service prices or charging standards, units can take service as the cost accounting object. Specific guidelines for hospital industry cost accounting shall be formulated by the Ministry of Finance in accordance with these guidelines. " The Interim Measures for Cost Accounting of Public Hospitals (Draft for Comment) issued in May 2020 put forward: "Hospitals should accurately calculate the cost of medical services and provide basis and reference for government pricing agencies and relevant units to formulate relevant prices or charging standards.
DRG cost accounting is a process of collecting, distributing and calculating DRG cost by activity-based costing and superposition method, which is based on factors such as patients’ age, sex, hospitalization days, clinical diagnosis, symptoms, surgery, disease severity, complications and outcomes, and divides patients into several disease diagnosis related groups. Standardize the classification of medical service charges, and the medical service charges promulgated by local government departments should be classified according to the medical income stipulated in the government accounting system, and at the same time classified according to the charging category on the first page of medical records.
DRG cost accounting is a process that takes DRG groups as the accounting object, collects related expenses according to a certain process and method (cost-expense ratio method or medical service item superposition method) and calculates the average cost of each group. After the reform of DRG payment mode, the hospital is faced with the following changes: the charging and payment policies have changed, the income-generating model has changed (scientifically controlling fees and increasing the balance), the medical insurance audit and reimbursement process has changed, and the pricing unit has changed (by item into groups).
Focusing on the principles of unified grouping, unified coding and unified cost accounting standards, learning from the successful experience of DRG payment in typical countries is the key to popularize DRG payment in combination with China’s national conditions. At the national level, a unified hospital cost accounting standard is issued to clarify the quality requirements of hospital cost data, which lays a good foundation for collecting comparable cost data, following the principle of similarity in resource consumption, improving the accuracy of DRG grouping and building a national cost database supporting DRG payment.
Design of DRG payment implementation scheme
The basic conditions for implementing DRG payment in hospitals include: unified disease diagnosis coding and surgical operation coding, up-to-standard medical record quality, relatively standardized diagnosis and treatment process, interconnected information systems, capable management team and sound cooperation mechanism. The implementation process of DRG payment includes environmental investigation and preparation in advance, establishment of working groups (expense and cost accounting group, DRG expert group, supporting policy development group, system construction support group, communication and coordination support group, etc.), unified interface specification, standardized medical record home page, standardized diagnosis, clear coding requirements, data extraction (cleaning, standardization, Measurement weight, rate-related indicators, etc.), training, scheme formulation, system transformation, information collection, demand document formation, system design (medical insurance fund settlement list, grouping device, settlement system, management monitoring system), system operation (simulation, optimization and trial operation), daily maintenance and quality control of the first page of medical records.
Among them, data collection and integration, the establishment of project implementation team, basic data management, revenue analysis data modeling, cost accounting rules modeling, and the establishment of breakeven analysis model are the prerequisites for cost accounting. According to the national pilot requirements of DRG payment, referring to the National Pilot Work Plan of Payment by Disease Diagnosis Related Grouping (DRG) of Wuhan Basic Medical Insurance (No.1 [2019] of Wuyi Medical Service), tongji hospital summed up the experience of full-cost accounting in departments, formulated the implementation plan of DRG payment in hospitals, defined the project objectives, and guided relevant departments to follow the expected objectives, time schedule and key tasks in each stage. Strengthen the informatization and standardization of data collection such as clinical medical records and fees, promote the first page information and data management of medical records, and calculate the relevant indicators of DRG grouping, start the cost accounting of projects and diseases, and promote the refined management and quality connotation development of hospitals.
The start-up of DRG prepayment reform should adhere to the high-level lead, multi-sectoral coordination, high-level lead in reform implementation and collaborative participation of stakeholders, which has an important impact on the implementation and promotion of reform. The hospital set up a cost accounting leading group headed by the president, with the chief accountant and the vice president in charge of finance as the deputy heads. The members include the heads of medical, nursing, medical record, information, medical insurance, statistics, finance, price and other departments, and are responsible for project management (see Table 1).
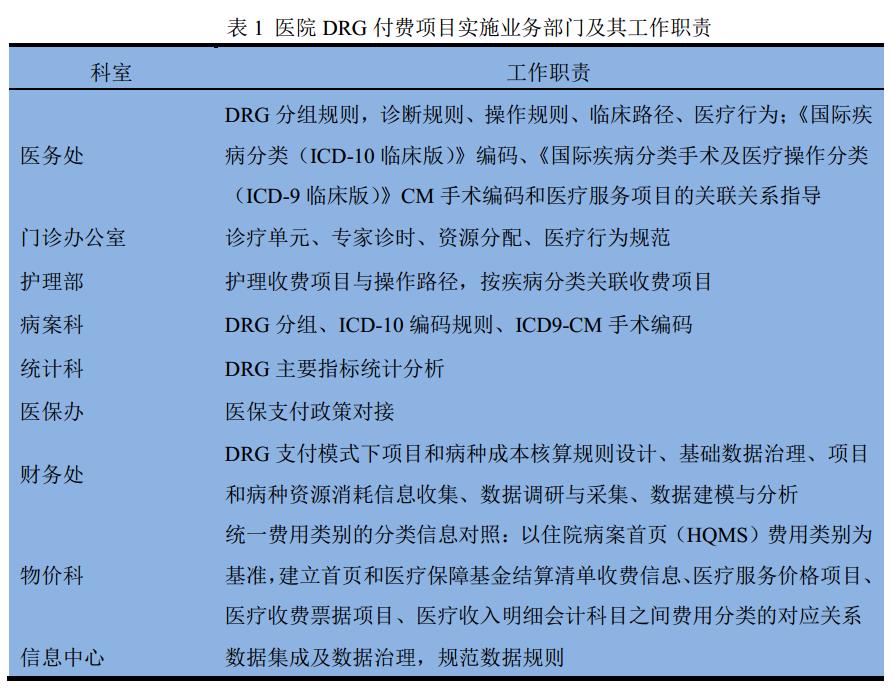
Set up an expert group of DRG payment business, which is composed of clinical medical experts, medical technology experts, nursing experts, medical record management experts, price management experts, etc., to guide the accounting of medical service project cost, disease cost and DRG cost, confirm the medical service process and corresponding health resource consumption parameters, and ensure the convergence of accounting objects, accounting services and medical services.
The software company is mainly responsible for data integration, data cleaning, data analysis, DRG cost analysis, project and disease cost accounting software development, department cost information investigation, project disease resource consumption information collection, etc. The output objectives of DRG paid projects include:
(1) Analysis of department income based on patient expenses: analysis of department income, project income, DRG income and medical group income in the last year, dynamic analysis and monitoring of DRG expense consumption, and combing and monitoring the details of high-frequency surgery or operation charges in the last year by using big data.
(2) The analysis of project and disease composition: the cost accounting and analysis of last year’s project, DRG grouping cost accounting and analysis, and disease cost accounting and analysis.
(3) Profit and loss analysis: the profit and loss analysis of medical services in the hospital, clinical departments and medical technology departments last year, the profit and loss analysis of DRG group in the hospital, and the comparison of DRG group’s cost consumption with the provincial average; Profit and loss analysis of diseases in the whole hospital, and profit and loss analysis of internal services such as laundry and disinfection fees in medical auxiliary departments such as laundry room and supply room
Practice of hospital cost accounting under DRG payment system
When hospitals conduct cost accounting under the DRG payment system, according to the principle of "who benefits, who bears", they collect and allocate various costs and expenses, so as to match each medical income with the costs and expenses for obtaining corresponding income, so as to determine the profit and loss of projects, diseases and DRG groups. When the hospital takes the medical service items stipulated in the unified charging standard as the cost accounting object, the data collection is refined to the items that can be charged separately, and the detailed data such as material consumption and depreciation occurred in the department during the project accounting period are collected according to the source of funds.
When the DRG group is taken as the cost accounting object, the cost is collected and the labor cost, material cost and drug cost consumed by medical services for various diseases are accounted. Cost accounting data collection includes: income data integration and analysis, cost data integration and analysis, and basic data needed for cost accounting are collected according to the standard path. According to the requirements of government accounting system, collect detailed data of outpatient and inpatient medical income.
1. Basic data governance of cost accounting
The basic data management of cost accounting includes: (1) unifying the classified information of expense categories, and establishing the corresponding relationship among expense categories on the first page of medical records, medical insurance settlement list, medical receipt list and accounting income subjects, so as to facilitate the collection of medical income data according to clinicians, execution units and medical service items. (2) Classification of medical service projects, which are divided into general projects and specialized projects in the whole hospital. (3) Cleaning of sanitary material warehouse, medicine warehouse, equipment warehouse and personnel warehouse, etc.
1.1 Unified classification information of expense categories
Different versions of medical service price items are implemented in different places, which are mainly divided into two versions: National Medical Service Price Item Specification (2001 Edition) and National Medical Service Price Item Specification (2012 Edition). The current medical service charge category will gradually transition to the category of National Medical Service Price Item Specification (2012 Edition). The first page of medical record contains all the information needed to implement DRG, and the cost classification is one of the basic data of DRG payment.
The Notice of the Office of the State Medical Insurance Bureau on Printing and Distributing the Specification for Filling in the Settlement List of the Medical Insurance Fund (No.20 [2020] of the Medical Insurance Office) points out: "The filling in the settlement list of the medical insurance should accurately reflect the information such as the diagnosis and treatment of patients and medical charges. Among them, the diagnosis and treatment information data mainly comes from the home page data of hospitalization medical records, and the index caliber of medical charge information data is consistent with the unified medical hospitalization bill information of the Ministry of Finance, the National Health and Wellness Commission and the National Medical Insurance Bureau. "
As a patient grouping scheme based on information related to diagnosis and treatment, DRG is based on the home page data of hospital medical records and its related disease classification and coding standards for diagnosis and treatment. The standardization of medical charging items and cost items and the consistency of data bases among hospitals can enhance the comparability of charging and cost among similar hospitals [10].
Uniform fee categories, The purpose is to refer to the Notice of the Ministry of Health on Revising the Home Page of Hospitalization Medical Records (Wei Yi Zheng Fa [2011] No.84), the National Medical Service Price Project Specification (2012 Edition), and the Notice on Comprehensively Implementing the Management Reform of Electronic Bills for Medical Charges (Caizong [2019] No.29). Notice on Printing and Distributing Supplementary Provisions and Cohesive Provisions for Hospital Implementation of Government Accounting System-Accounting Subjects and Statements of Administrative Institutions (Cai Shui [2018] No.24), Notice on Printing and Distributing National Pilot Technical Specifications and Grouping Scheme for Disease Diagnosis Related Grouping (DRG] No.36), The Notice of the State Medical Insurance Bureau on Printing and Distributing the Coding Rules and Methods of Medical Insurance Designated Medical Institutions and Other Information Services (No.55 [2019] of the Medical Insurance Bureau) and the Notice of the Office of the State Medical Insurance Bureau on Printing and Distributing the Settlement List of the Medical Insurance Fund (No.20 [2020] of the Medical Insurance Bureau), and the comparative relationship between the medical record home page and the medical service price items, medical insurance fund settlement list, charging bills and income subjects is established, so as to realize the inter-hospital comparison.

1.2 the underlying data construction of cost elements
Hospital resource consumption is divided into human resource consumption, tangible assets such as buildings, equipment, materials and products, intangible assets such as application software and other expenses according to cost factors. The underlying data of cost elements include:
(1) Personnel database: including accounting unit (department), medical group, job number, personnel name, personnel title and personnel salary. Clear personnel positioning rules, according to the project, disease collection personnel who play the corresponding role. For multi-role personnel who serve multiple accounting units in the same accounting period, their labor costs are shared among service departments according to attendance and workload, and allocated to relevant disease groups according to the working hours of participating in the disease groups.
(2) Material warehouse: including accounting unit, material name, quantity to be collected, material unit price, material total price, and whether it is chargeable material (in a certain department, a material is defined as chargeable material or non-chargeable material; The materials charged for a certain project can automatically correspond to the project).
Cleaning of sanitary materials warehouse, including cleaning of sanitary materials catalogue warehouse, classifies and accounts sanitary materials according to factors such as pricing and non-pricing charges, high value and low value, disposable and recyclable use. Establish the classification rules of chargeable and non-chargeable sanitary materials, the corresponding relationship between materials allowed to be charged separately and medical service items (classify disposable medical consumables according to the categories of medical service items, including disposable medical materials for examination of diagnostic operation items, disposable medical materials for surgery and interventional operation, disposable medical materials for treatment in non-surgical treatment, traditional Chinese medicine or clinical physical therapy and rehabilitation items), and the corresponding relationship between materials and DRG group, and collect the income of materials that can be charged separately according to clinicians and execution units.
Establish the corresponding relationship between the charging items of sanitary materials and the material code, so as to write off the cost of sanitary materials of different materials, different patients (diseases) and different accounting units according to the benefit principle. The charging rules of medical consumables that can be charged separately are complicated, including "one-to-one" charging, charging at the same price according to different product specifications, packaging charging, and group charging. It is a necessary basic work to carry out the fine management of the whole process of charging medical consumables, carry out the associated query of DRG patients’ expense list, consumables and medical service items, and realize the matching of consumables dictionary and HIS charging items in the material management system.
(3) Drug library: including accounting unit, drug name, quantity collected, drug unit price, and drug total price (required for disease cost and DRG cost accounting). Collect drug income data according to drug quality regulations, outpatient service and hospitalization, accounting unit and billing doctor.
(4) Asset library: including accounting unit, name of fixed assets (intangible assets), original value of assets, depreciation (amortization) years and depreciation expense (amortization expense of intangible assets). Establish the corresponding relationship between medical service items and medical equipment, and make statistics on the workload and income of large-scale equipment inspection according to date, specialty (ward), patient, equipment number, inspection fees and technicians. After the charging items of medical services correspond to the large-scale medical equipment, the list of DRG patients’ fees and medical services will be jointly checked.
(5) Project library: including the classification of all price charging items in the hospital:
① The first dimension: distinguish between general medical services and specialized medical services. According to the types and cases of medical service price items, the types of medical service items carried out by clinical departments can be classified and counted as "general items of the whole hospital (items commonly used by multiple departments, such as comprehensive medical services, physical therapy and rehabilitation items)" and "specialist items", so that all medical costs can be reasonably shared and the costs of departments and single items can be accurately calculated. Understand the development of departmental projects, monitor the charging dynamics, and increase the proportion of medical income. Sort out departments to carry out disease-related projects, monitor income, and tap operational potential.
② The second dimension: it is divided into items that need equipment and materials, and items that don’t need equipment and materials (such as bed fee, heating and cooling fee, registration fee, oxygen fee, etc.).
(6)HIS data: including accounting unit, patient’s hospitalization number, detailed list of all patients’ charges in the hospital, and hospitalization days.
(7)DRG grouping: including time consumption index and expense consumption index of chief physician, deputy chief physician and patient.
(8) Hand anesthesia system data: including operation name (ICD-10 or ICD9-CM), corresponding charging items, patient’s hospitalization number, operation duration, operator, anesthetist, instrument nurse and visiting nurse.
1.3 clear cost data integration requirements
For cost data, it is necessary to find the relationship between personnel, materials, drugs, assets, medical record home page, surgical anesthesia, HIS, DRG grouping and other system-related data, establish data corresponding rules, and integrate data.
(1) Rules for integration, allocation and accounting of labor costs. Personnel orientation: ① the relationship between employees and accounting unit and medical group; ② The level of accounting of inpatient departments: individual-medical group-ward-specialist-hospital area. ③ Accounting level of outpatient department: individual-specialist-hospital area. ④ The corresponding relationship between medical service items and human resources consumption.
(2) Accounting rules for cost integration and allocation of sanitary materials. Clarify the relationship between chargeable sanitary materials and DRG group, and the relationship between non-chargeable materials and medical service items or DRG group.
(3) The integration, allocation and accounting rules of equipment depreciation, and the corresponding relationship between special equipment and medical services.
(4) The integration, allocation and accounting rules of other operating costs, and the corresponding relationship between cost accounting subjects and medical service items.
(5) Rules for cost integration, allocation and accounting of operation items such as surgery and treatment. For operation items such as surgery and treatment, try to record and account the operation cost according to the top medical service items with the highest fees in each specialty.
(6) The rules of cost integration, allocation and accounting of DRG group, establishing the corresponding relationship between DRG group and medical service project, and accounting the DRG composition according to the project cost accounting results.
2. Cost analysis data modeling
Cost analysis data modeling includes:
(1) Revenue analysis of medical services in the whole hospital: visual data display and information associated query.
(2) Revenue analysis of medical service items in departments: visual data display and information associated query, and optimized display forms according to the requirements of departments.
(3) Income analysis of high-frequency surgery: visual data display and information associated query.
(4) Analysis of charging operation after price dynamic adjustment: visual data display and information associated query.
(5) Cost analysis of DRG group in the whole hospital: visual data display and information associated query.
(6) Comparison of DRG expenses and payment standards in the whole hospital: visual data display and information associated query. Analyze the differences in payment and charges of various disease groups in the hospital, do a good job in the analysis and monitoring of the disease structure in the hospital, and rationally plan the disease revenue and expenditure structure according to the medical insurance payment policy.
(7) Comparison between DRG expenses of departments and payment standards: visual data display, information associated query and department feedback. According to the comparison between the average expenses of each DRG group in each department last year and the average expenses of the same group of data in the province, analyze and predict the impact of DRG payment on hospital income, and assist departments to adjust and optimize the disease structure. The average cost of each DRG group can reflect the degree of disease difficulty and resource consumption to a certain extent.
(8) Standardized charging template for diseases: establish a charging template for diseases based on big data, and implant feasible schemes into the information system after investigating and soliciting opinions from departments.
3, cost accounting rules and knowledge base construction
DRG cost accounting generally adopts the superposition method of medical service items and drug and material costs. Therefore, the accuracy of medical service project cost accounting determines the fineness of DRG cost accounting, and the construction of project cost accounting rule knowledge base is very important. According to the cost attribute and business type, and according to the relationship between input and output, we classify and model the project cost accounting rules:
(1) Activity-based Costing Accounting Model: Through the method of "field investigation", the standardized operation is investigated in departments and organized into an operation library. According to the operation motivation, the resource consumption of each operation (such as labor hours, equipment hours, single material consumption, etc.) is combed and recorded, and the related costs of medical service project execution departments are reasonably shared. This rule is generally applicable to inspection items, operation items such as surgery and treatment with high degree of standardization.
(2) Cost coefficient proportional method model: On the basis of department cost accounting, according to the resource consumption motivation, rules such as income distribution coefficient, personnel proportion coefficient, occupied area proportion coefficient, working hours coefficient and workload coefficient can be set to share the public cost of the whole hospital or execute the department cost. This rule is generally applicable to medical services generally carried out in the whole hospital, such as bed fees, nursing fees, examination fees, etc. Project cost accounting rules are greatly influenced by diagnosis and treatment habits and management fineness, so it is necessary to consider the combination of standardized configuration and mobile configuration in the construction of knowledge base.
4. DRG component cost analysis
The cost analysis report mainly includes DRG grouping schedule, cost structure table, profit and loss analysis table, profit and loss sorting analysis table and so on. Using the cost accounting results, according to the needs of different managers, it provides them with visual breakeven analysis views of the whole hospital, departments, medical groups and DRG groups. From the aspects of the hospital as a whole, different departments in the same disease group, different disease groups in the same department, and different doctors (groups) in the same disease group, aiming at the composition and change of expenses, the departments, doctors (groups) and disease groups with unreasonable expenses were found by using structural analysis, trend analysis and factor analysis.
The results of cost accounting can be applied to the pricing of medical services, and the medical security department will take the average cost of the hospital as an important basis for pricing when setting the charging price of DRG patients. Hospitals can accurately analyze the reasonable pricing range and cost structure changes of disease components through horizontal and vertical comparisons between hospitals and disease groups, actively participate in medical insurance negotiation, and also provide accurate basis for intelligent supervision of medical insurance.
It is helpful for government departments and hospital managers to know the actual situation of resource consumption in providing medical services by carrying out cost analysis to determine the business volume and total guaranteed income of breakeven point in the normal development of medical services, so as to provide reference for building a scientific and reasonable medical service pricing and dynamic adjustment mechanism, reasonably compensating medical costs (price charge compensation, government financial classification compensation, medical insurance fund compensation, and optimizing resource allocation) and improving resource utilization efficiency.
In a word, the characteristic of DRG payment is that its pricing is related to the clinical diagnosis of each case, but not directly related to the actual cost of the case. Under the DRG payment system, hospitals are compensated and paid at a fixed price, which encourages hospitals to provide medical services at a cost lower than the fixed price economically and keeps the difference between the fixed price and the cost. The difference below the payment amount forms the surplus of the hospital, and the part above the payment amount forms the loss borne by the hospital. If the hospital’s cost accounting is not perfect, the cost and cost information are incomplete and inaccurate, it will increase the risk of the hospital’s operating cost paid by DRG.
The actual medical expenses of some disease groups are higher than those paid by medical insurance DRG group. After DRG payment is implemented, the hospitalization income of these disease groups will be reduced. When hospitals are faced with fixed prices, it is necessary to minimize the cost of treating patients. According to different case combinations, the hospital accepts compensation, prompting the hospital to provide the most effective service according to the payment requirements of DRG. DRG price can not only promote the hospital to improve its internal efficiency, but also enable the hospital to make use of economies of scale in service supply.
Carrying out DRG cost accounting is the requirement of promoting the reform of DRG payment method and promoting the hospital to actively control costs. After paying by DRG, the hospital’s income becomes quantitative, and it is necessary to make a breakthrough in cost control to obtain surplus. Only by finding out the treatment cost of each DRG can we make clear the direction of operation and management and provide data support for hospital decision-making.
Cost accounting personnel should change the previous concept of cost accounting, comprehensively sort out the cost accounting items, refine the indirect cost allocation parameters, and objectively reflect the cost status of drugs, consumables, medical technology, nursing and management for each patient and each DRG group. DRG cost accounting is a long-term and arduous task, and it is the cornerstone of promoting hospital fine management, which requires good cooperation between hospital cost management related departments and clinical departments.
The steady promotion and continuous exploration of DRG cost accounting can make a set of accounting standards, improve internal management, establish a set of standardized procedures, cultivate a high-quality team, actively apply the new situation of medical insurance purchase service, improve cost awareness, standardize diagnosis and treatment behavior, and rationally allocate medical resources.
Follow-up research can make statistical analysis of big data, evaluate the pilot work, form an evaluation report of DRG effect, and give suggestions for improving accounting work in the next step. With the deepening of the pilot, DRG cost accounting will be more comprehensive, accurate and mature in future exploration and practice.
The author introduces:
Dai Xiaozhe, deputy director of tongji hospital Finance Department affiliated to Tongji Medical College of Huazhong University of Science and Technology, is a senior accountant. National accounting leader, economic management leader of the National Health and Wellness Commission, cooperative researcher of the Institute of Government Accounting of Zhongnan University of Economics and Law, and part-time teacher of the School of Medicine and Health Management of Huazhong University of Science and Technology. He has published many articles in core journals such as chinese health economics, Medicine and Society, and undertaken many research work by the Ministry of Finance, the Finance Department of the National Health and Family Planning Commission, and the Medical Accounting Society of china health economics association and China. He has won the third prize of scientific and technological progress in Hubei Province, the second prize of scientific and technological innovation in China Hospital Association, and his achievements have been appraised as advanced in China. A number of research work won the title of excellent bidding subject in china health economics association.
-THE END-

